This retrospective observational diagnostic study was conducted at Medipol University under the approval of the non-interventional clinical research ethics committee. The study aimed to analyze electronic records of asymptomatic female patients aged 40 years and above who underwent breast tissue screening via Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) at the Breast Imaging Unit of the Department of Radiology at Medipol Mega University Hospital between March 2022 and January 2023.
A total of 2521 DBT examinations were retrospectively analyzed, with a mean age of 55 years among the patients. The study utilized DBT images captured using Siemens Mammomat Revelation and focused on the left mediolateral oblique (MLO) views that displayed adequate levels of pectoral muscle. The selection criteria included cases categorized as Breast Imaging-Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) 1, 2, or 3 and excluded cases with suspicious masses (BI-RADS 4, 5, 6) or prior cancer treatment history.
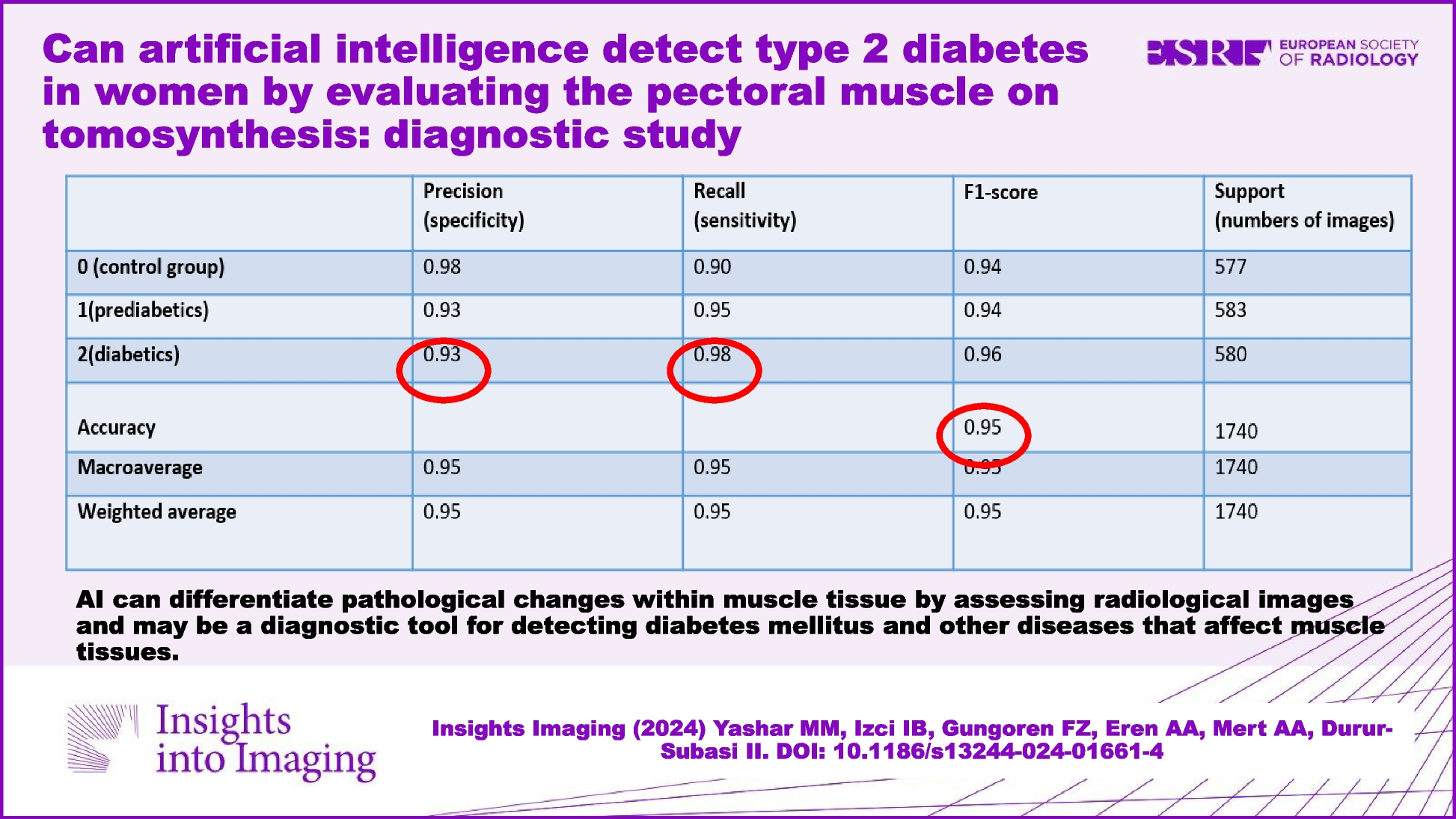
The study design involved collecting left DBT images and corresponding same-day HbA1c% values for diabetes screening. Patients were categorized based on their HbA1c levels as normal, prediabetic, or diabetic. The images were further categorized into three age groups: 40–49 years, 50–59 years, and 60 years and above. A minimum of 1000 images per category per age range was aimed for analysis to train an Artificial Intelligence (AI) model to differentiate between the groups effectively.
The dataset was split for training and testing the AI model, utilizing data augmentation techniques to enhance model accuracy. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) were employed, with the EfficientNetB5 architecture utilized for transfer learning. The model was trained and evaluated using labeled images belonging to the three HbA1c categories. The model’s performance was assessed based on various metrics like precision, recall, and F1-score, with a focus on achieving a high accuracy rate to predict patients’ diabetes status effectively.
The study process integrated advanced technology and precise methodologies to improve diagnostic capabilities, showcasing a progressive approach towards leveraging AI in healthcare for enhanced patient outcomes.